Organizational Strategy & Performance
Definition of Organizational Strategy
In the Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) world, Organizational Strategy is the plan that has been defined to deliver the mission and achieve the vision defined by the leaders of the organization.
It involves the definition or review of the mission and vision statements, as well as the steps that need to be taken to achieve them.
An Organizational Strategy helps everybody understand where the business is going and how their work can impact those plans.
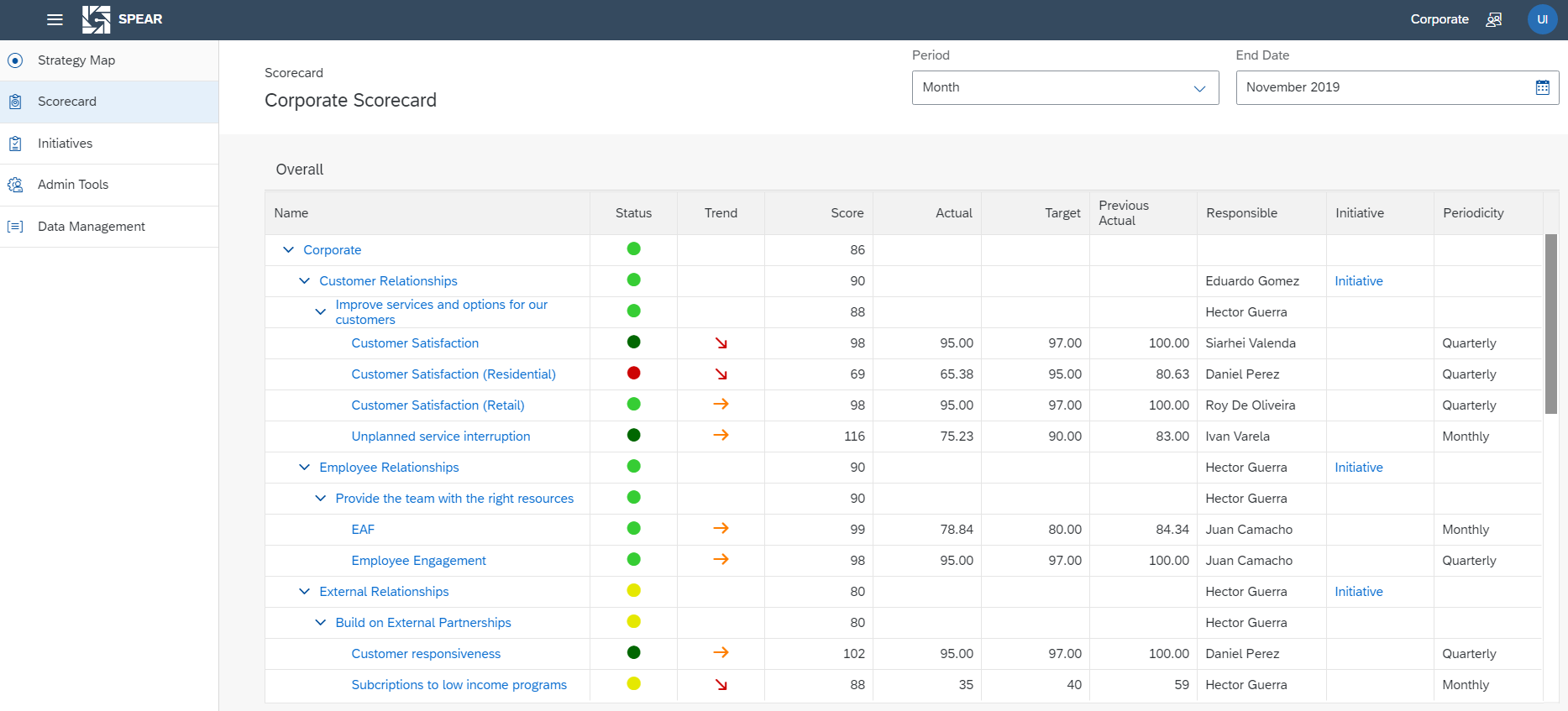
Organizational Strategy Process
1. Strategy Development
In many cases the process starts with an executive retreat where the top priorities are set.
Some characteristics of these meetings are:
- They can be managed internally or with the assistant of an external facilitator.
- They could follow a top down approach: which is more common and forward looking. In this the leaders define the guidelines and initial priorities and then more players (groups or individuals) are involved to cascade those to lower levels of the organization.
- They could follow a bottom up approach: which is less common and typically focused on tackling current challenges. Here the different areas provide their key priorities and then the leaders consolidate the priorities into a small set that will be showcase in the strategic plan moving forward.
- As a result of the process they could also get the short and long term goals or strategies.
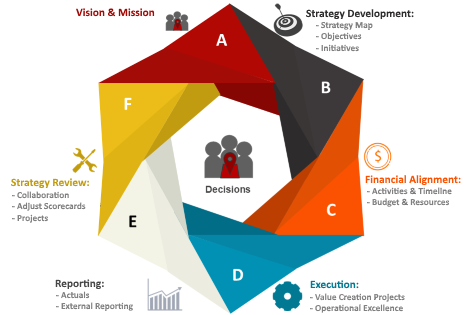
After those priorities are set, the different areas are brought in to start setting goals, strategies and targets.
The goals, strategies and targets included in the Organizational Strategy could be in form of projects (initiatives), with Milestones that need to be achieved by specific dates. They also can be exposed as Key Performance Indicators that compare those targets against the actual numbers for a specific period of time in order to measure results.
2. Financial and Operational Alignment
Based on the result of the previous step, the financial and operational resources are allocated and the Strategy is linked to the budget process.
3. Execution
Once the budget to execute the plan is approved, the organization starts the execution, where results are gathered and compared with targets to evaluate performance and take actions based on those results.
4. Reporting and Review
As a last step the organizations prepare reports, provide analytics and the Strategy is reviewed and/or adjusted.
Challenges of Organizational Strategy
A very typical scenario results with a Strategic Plan as a PDF document somewhere on a website and the employees doing the same thing they have been doing from years.
It is hard to create a Strategic Planning culture and there are many challenges.
To learn more check our post about some of the most common challenges and some recommendations to work around them.
Software as an option
In many cases, a tool is very useful to help exposing that strategy in a structured way and also publishing that information to other users in the organization.
A software that manages Organizational Strategy can also assist with the collection of information on a regular basis (manual or automated) and provide insights into how the individuals, department and overall organization is performing.
Again, the idea is not to expend our resources collecting data and preparing reports, but to allocate them in order to tackle the priorities defined, achieve targets, mitigate risks or timely react to any challenges.
Check below some of the tools we have used to deliver this value to our customers
Cipher's Advantage
Having successfully implemented many Organizational Strategy projects, we can help in reviewing the current plan to help in standardizing the process. This means reducing the time spent to collect information and report results in a way people can easily understand the performance without spending too much time.
Case Study
Nebraska Public Power District's CEO presents the year end performance results to the Board of Directors. Their Strategic Plan follows the Balanced Scorecard methodology and their CEO is using the strategy map to show their Priorities and Key Performance Indicators
Watch the specific section of the Board of Director's meeting
Applications
SPEAR
SPEAR stands for Strategy, Planning, Execution and Reporting.
It helps organizations close the gap between strategy and execution, by allowing them to publish their corporate strategy and showing how it cascades to the different levels of the organization, setting strategic goals and monitoring the performance towards those objectives to take the necessary actions and align resources accordingly.
SAP Sustainability Performance Management (SuPM)
The SAP BusinessObjects Sustainability Performance Management application enables organizations to manage their economic, social and environmental performance.
Predefined content is offered out-of-the-box including a list of KPIs provided by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
SAP Strategy Management (SSM)
SAP Strategy Management allows organizations to configure their Strategy, cascade it down to all the areas and monitor performance with KPIs and Strategic Initiatives.
SSM Provides a set of pre-defined view such as Scorecards and Initiatives diagrams along with customizable Strategy Maps and Ad-hoc reports.
SAP Supply Chain Performance Management (SCPM)
SAP BusinessObjects Profitability and Cost Management (SPCM) is a highly scalable application that enables the business users to improve profitability by different parameters such as products, customers and channels.
Organizations can configure Scorecards based on the Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) model while interacting with an intuitive interface.