[big_title2]What is SWOT Analysis?[/big_title2]
The SWOT Analysis is a framework that allows an organization perform an analysis on internal and external factors that can help shape or influence the future of the organization.
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
Some people claim it was first presented during a series of conventions of Stanford Research Institute back in the 60s and 70s but nobody has claimed the creation of this Analysis.
[big_title2]How does the SWOT Analysis work?[/big_title2]
Organizations need to put together a two by two matrix and each of the categories of the SWOT analysis will be represented by a quadrant. On each quadrant you need to list all the items that fall into the corresponding category.
At the end you should have a list of all your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
You will later match the elements on that list to generate goals that will drive the actions of the organization.
[big_title2]How do you get the data for the SWOT Analysis?[/big_title2]
SWOT Analysis is not the result of just a group brainstorming ideas and opinions, although this is part of it. As we explained earlier, the SWOT Analysis combines internal and external factors, so the data should be coming from both internal and external sources.
We can also divide the categories of the Analysis.
Strengths and Weaknesses as internal, as they are things we can control.
Opportunities and Threads as external, since those include factors that are out of our hands but we can still react or prepare for their impact.
To get the data for internal categories you can use:
- Current Performance: check your scorecards and dashboards to list those items in which you excel or struggle.
- Customer Surveys: ask your customers’ feedback about your skill and the performance of the work delivered.
- Employee Surveys: ask your employees about their own skills or the team skills and experiences.
- Financial information: check what resources, assets and budget you have so you know the current state of the organization.
The idea is to list those resources, processes or main capabilities we have that will represent a Strength or a Weakness.
To get the data for external categories you can use:
- Industry Information: this is related to the trends, challenges, etc. within your market.
- Competitors: check what others are doing as their actions can also impact your future.
- Environmental information: this could include financial indicators such as Interest Rates, Market Performance, among others.
[big_title2]How to use a SWOT Analysis?[/big_title2]
In order for a SWOT Analysis to be valuable, it needs to drive actions within the organization. Ideally what you want to do is:
- Make the most of your Strengths
- Minimize your Weaknesses
- Invest or capitalize on your Opportunities
- Identify your Threats
This is the right moment to brainstorm what you can do to achieve all of the above.
Also within the SWOT Analysis you should match items from different categories the following way:
- We want to use our Strengths to capitalize Opportunities
- We also want to use our Strengths to deal or eliminate a Weakness.
- We can evaluate if there are any opportunities that can help us deal with any of our Threats.
SWOT Analysis is often one of the first steps in building a Strategic Plan, as it gives you the current state and it can also generate the future goals and areas of focus.
[big_title2]Example of a SWOT Analysis:[/big_title2]
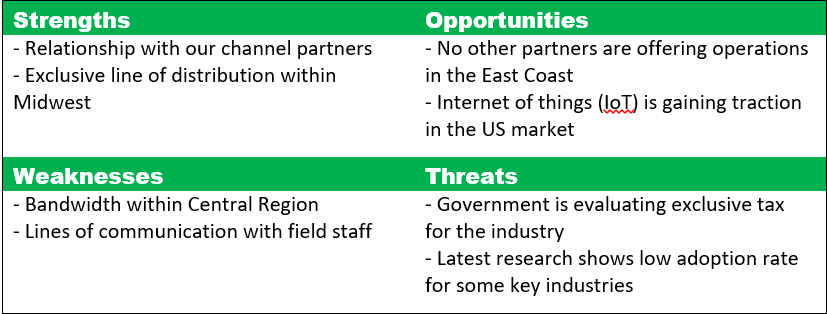
Here you have a simple example of the SWOT Analysis
Example of SWOT Analysis made by the US Department of Agriculture